20172304 蓝墨云实验哈夫曼树
实验要求
- 设有字符集:S={a,b,c,d,e,f,g,h,i,j,k,l,m,n.o.p.q,r,s,t,u,v,w,x,y,z}。 给定一个包含26个英文字母的文件,统计每个字符出现的概率,根据计算的概率构造一颗哈夫曼树。 并完成对英文文件的编码和解码。
- 要求:
- (1) 准备一个包含26个英文字母的英文文件(可以不包含标点符号等),统计各个字符的概率
- (2) 构造哈夫曼树
- (3) 对英文文件进行编码,输出一个编码后的文件
- (4) 对编码文件进行解码,输出一个解码后的文件
- (5) 撰写博客记录实验的设计和实现过程,并将源代码传到码云
- (6) 把实验结果截图上传到云班课
哈夫曼编码
- 哈夫曼编码(Huffman Coding),又称霍夫曼编码,是一种编码方式,哈夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。Huffman于1952年提出一种编码方法,该方法完全依据字符出现概率来构造异字头的平均长度最短的码字,有时称之为最佳编码,一般就叫做Huffman编码(有时也称为霍夫曼编码)。
原理
这个老师上课说过。首先确定文件中各个字符的概率然后将其。按照概率大小。将概率小的放在离根节点较近的地方。
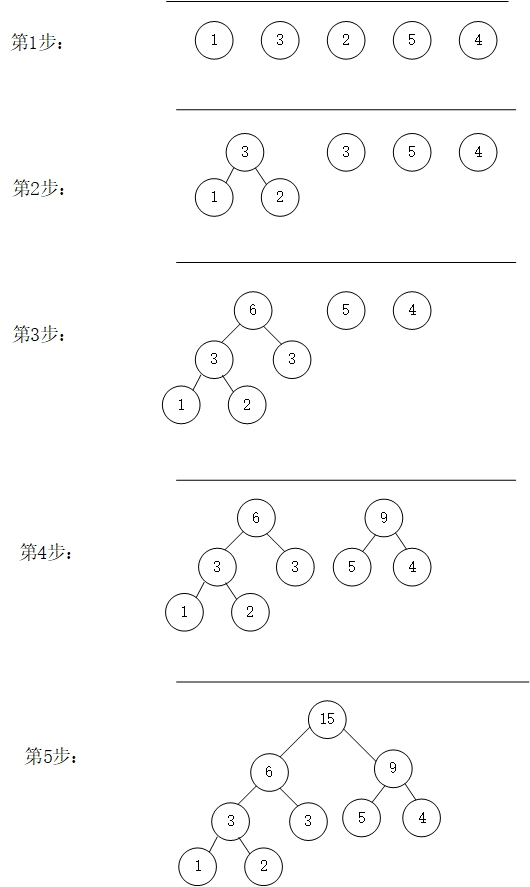 这里用数字来代表字符的概率然后,首先将概率最小的两个字符放到一起,将它们的概率合成父结点的概率,然后父结点参与比较再次在备选集中找到比较小的两两结合,然后再次合成父结点的概率。
这里用数字来代表字符的概率然后,首先将概率最小的两个字符放到一起,将它们的概率合成父结点的概率,然后父结点参与比较再次在备选集中找到比较小的两两结合,然后再次合成父结点的概率。 具体实现哈夫曼树
因为哈夫曼需要考虑到父结点的影响,所以定义了相关的左孩子右孩子的方法。
package HuffmanTree;public class HNode { /** * 节点类 * @author LiRui * */ public String code = "";// 节点的哈夫曼编码 public String data = "";// 节点的数据 public int count;// 节点的权值 public HNode lChild; public HNode rChild; public HNode() { } public HNode(String data, int count) { this.data = data; this.count = count; } public HNode(int count, HNode lChild, HNode rChild) { this.count = count; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; } public HNode(String data, int count, HNode lChild, HNode rChild) { this.data = data; this.count = count; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; } } - 构造哈夫曼树
- 哈夫曼树的构造,并不需要像创建二叉树的那么多的方法,满足形成哈夫曼编码的部分就好。分享的那篇博客有相关的内容,我们只需要在此基础上添加每次创建的的编码值就可以,左侧0右侧1就可以。
- 创建树,先将结点进行排序,利用结点类中实现的比较方法,分别将左孩子定义为列表中的倒数第二个,因为左侧编码为0,所以让该结点的编码为0;右孩子为列表中的倒数第一个,因为右侧编码为1,所以让该结点的编码为1,双亲结点根据所讲内容为左右结点权重相加之和,把双亲结点加入列表中,然后删除倒数两个结点并添加双亲结点,再次进行循环,排序,不断从列表中把倒数两个结点删除,直至跳出循环,此时列表中的结点只剩一个,该结点的左右部分包含了所有按照编码进行添加的元素内容。
public HuffmanNode
createTree(List > nodes) { while (nodes.size() > 1) { Collections.sort(nodes); HuffmanNode left = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 2);//令其左孩子的编码为0 left.setCode("0"); HuffmanNode right = nodes.get(nodes.size() - 1);//令其右孩子的编码为1 right.setCode("1"); HuffmanNode parent = new HuffmanNode (null, left.getWeight() + right.getWeight()); parent.setlChild(left); parent.setrChild(right); nodes.remove(left); nodes.remove(right); nodes.add(parent); } return nodes.get(0); } 这个是构建哈夫曼树的具体流程,因为需要在结点已经连接之后在进行比较所以就将所有出现的字符放在一个链表里便于操作。具体的流程代码有详细介绍。
/** * 将出现的字符创建成单个的结点对象 */ private void creatNodes() { for (int i = 0; i < charList.size(); i++) { String data = charList.get(i).c + ""; int count = charList.get(i).num; HNode node = new HNode(data, count); // 创建节点对象 NodeList.add(node); // 加入到节点链表 } } /** * 构建哈夫曼树 */ private void creatTree() { while (NodeList.size() > 1) {// 当节点数目大于一时 // 4.取出权值最小的两个节点,生成一个新的父节点 // 5.删除权值最小的两个节点,将父节点存放到列表中 HNode left = NodeList.poll(); HNode right = NodeList.poll(); // 在构建哈夫曼树时设置各个结点的哈夫曼编码 left.code = "0"; right.code = "1"; setCode(left); setCode(right); int parentWeight = left.count + right.count;// 父节点权值等于子节点权值之和 HNode parent = new HNode(parentWeight, left, right); NodeList.addFirst(parent); // 将父节点置于首位 Sort(NodeList); // 重新排序,避免新节点权值大于链表首个结点的权值 } }
这个是对结点链表进行排序的类
/** * 升序排序 * * @param nodelist */ private void Sort(LinkedListnodelist) { for (int i = 0; i < nodelist.size() - 1; i++) { for (int j = i + 1; j < nodelist.size(); j++) { HNode temp; if (nodelist.get(i).count > nodelist.get(j).count) { temp = nodelist.get(i); nodelist.set(i, nodelist.get(j)); nodelist.set(j, temp); } } } }
下面介绍一个类这个主要的作用是统计各个字符出现的次数,也就是老师所说的概率,然后再进行排序。
private void getCharNum(String str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { char ch = str.charAt(i); // 从给定的字符串中取出字符 flag = true; for (int j = 0; j < charList.size(); j++) { CharData data = charList.get(j); if(ch == data.c){ // 字符对象链表中有相同字符则将个数加1 data.num++; flag = false; break; } } if(flag){ // 字符对象链表中没有相同字符则创建新对象加如链表 charList.add(new CharData(ch)); } } } 这是输出每个结点编码的类
private void output(HNode node) { if (node.lChild == null && node.rChild == null) { System.out.println(node.data + ": " + node.code); } if (node.lChild != null) { output(node.lChild); } if (node.rChild != null) { output(node.rChild); } } /** * 输出结果字符的哈夫曼编码 */ public void output() { output(root); } 这是编码的过程,主要原理是通过通过一个查找的方法不断地将传进的字符串在哈夫曼树中找到并返回他的哈夫曼编码最后在输出出来。
/** * 编码 * @param str * @return */ public String toHufmCode(String str) { for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) { String c = str.charAt(i) + ""; search(root, c); } return hfmCodeStr; } /** * * @param root 哈夫曼树根节点 * @param c 需要生成编码的字符 */ private void search(HNode root, String c) { if (root.lChild == null && root.rChild == null) { if (c.equals(root.data)) { hfmCodeStr += root.code; // 找到字符,将其哈夫曼编码拼接到最终返回二进制字符串的后面 } } if (root.lChild != null) { search(root.lChild, c); } if (root.rChild != null) { search(root.rChild, c); } } 解码部分与之类似。
- // 保存解码的字符串 String result=""; boolean target = false; // 解码标记 /** * 解码 * @param codeStr * @return */ public String CodeToString(String codeStr) { int start = 0; int end = 1; while(end <= codeStr.length()){ target = false; String s = codeStr.substring(start, end); matchCode(root, s); // 解码 // 每解码一个字符,start向后移 if(target){ start = end; } end++; } return result; } /** * 匹配字符哈夫曼编码,找到对应的字符 * @param root 哈夫曼树根节点 * @param code 需要解码的二进制字符串 */ private void matchCode(HNode root, String code){ if (root.lChild == null && root.rChild == null) { if (code.equals(root.code)) { result += root.data; // 找到对应的字符,拼接到解码字符穿后 target = true; // 标志置为true } } if (root.lChild != null) { matchCode(root.lChild, code); } if (root.rChild != null) { matchCode(root.rChild, code); } } 至于我上传的测试类中的统计概率的方法是借鉴的李馨雨同学的。
文件读写就太简单了相信学长学姐们都懂。感悟
哈夫曼是一种用于压缩的算法,是一种很实用的算法,但可能是个人能力的限制,在具体实现过程中遇见了很多困难,在具体的代码实现中,借鉴了很多网页和同学的思路。